Do you have questions about SEO? Maybe you’ve heard about how SEO can help you get more traffic and get higher rankings, but you’re not sure what it entails or what to focus on? This is the right place for you if that’s the case. Find out more about SEO by reading on.
Defining Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
To begin with, let’s clarify what SEO is. Basically, SEO stands for search engine optimization, which is the process of increasing the number of people who see your website when they search for it organically, editorially, or naturally. Remember, the higher your website ranks on search results pages, the more people will see it.
SEO involves a variety of activities, including:
- A method for identifying relevant keywords with a high potential for search traffic
- Content creation and optimization
- search engines and for users
- Including relevant links from high-quality sites
- Measuring the results
SEO is now considered an essential marketing tool.
Differences between paid and organic search

You must first understand the differences between organic, natural search, or SEO, and paid search. There are five key differences:
Position
As you might expect, paid search results are displayed at the top of search engine results pages, while organic search results are displayed beneath them.
Time
There are also many differences between paid and organic search when it comes to time. Paid search yields almost immediate results, sometimes in minutes, while organic search yields results that take weeks, months, and even years to appear. Therefore, organic search requires that you play a medium- to long-term game.
Payment
It’s easy to see that paid search is paid search. You pay-per-click (PPC) on a cost-per-click (CPC) basis, which means you pay a fee for every time someone clicks on your ad. Instead of relying on organic traffic to your website, you buy traffic for your page by paying Google to display your ad when your visitor searches for your keyword. In organic search, traffic is free, but it requires both resources and time investment.
ROI
When it comes to ROI, paid search is actually much easier to measure. That’s partly because Google provides more keyword data that you can use in your Google Analytics reports. Paid search can, however, stagnate or decrease over time. The ROI of organic search can be more difficult to measure, but it can often improve over time. Over the long term, organic search offers a very good return on investment.
Share of traffic
It’s estimated that 20% to 30% of searchers click on paid results, while 70% to 80% click on SEO results. As a result, organic results receive the lion’s share of clicks.
Similarities between paid and organic search
Both paid and organic search have similarities as well as differences:
Keyword research: The same search engine is used for both paid and organic searches, so you need keyword research for both.
Landing pages: A landing page is required for both kinds of search. A landing page for SEO needs to be attached to your website. A landing page for paid search can be the same as your organic landing page, or it can be a separate stand-alone page.
Traffic: It is important to remember that both paid and organic search aims to generate traffic that reflects user intent. In other words, if someone searches for information on Google or asks a question, they are in an active mindset, and as a result they are more likely to act upon finding it.
The Three Pillars of SEO
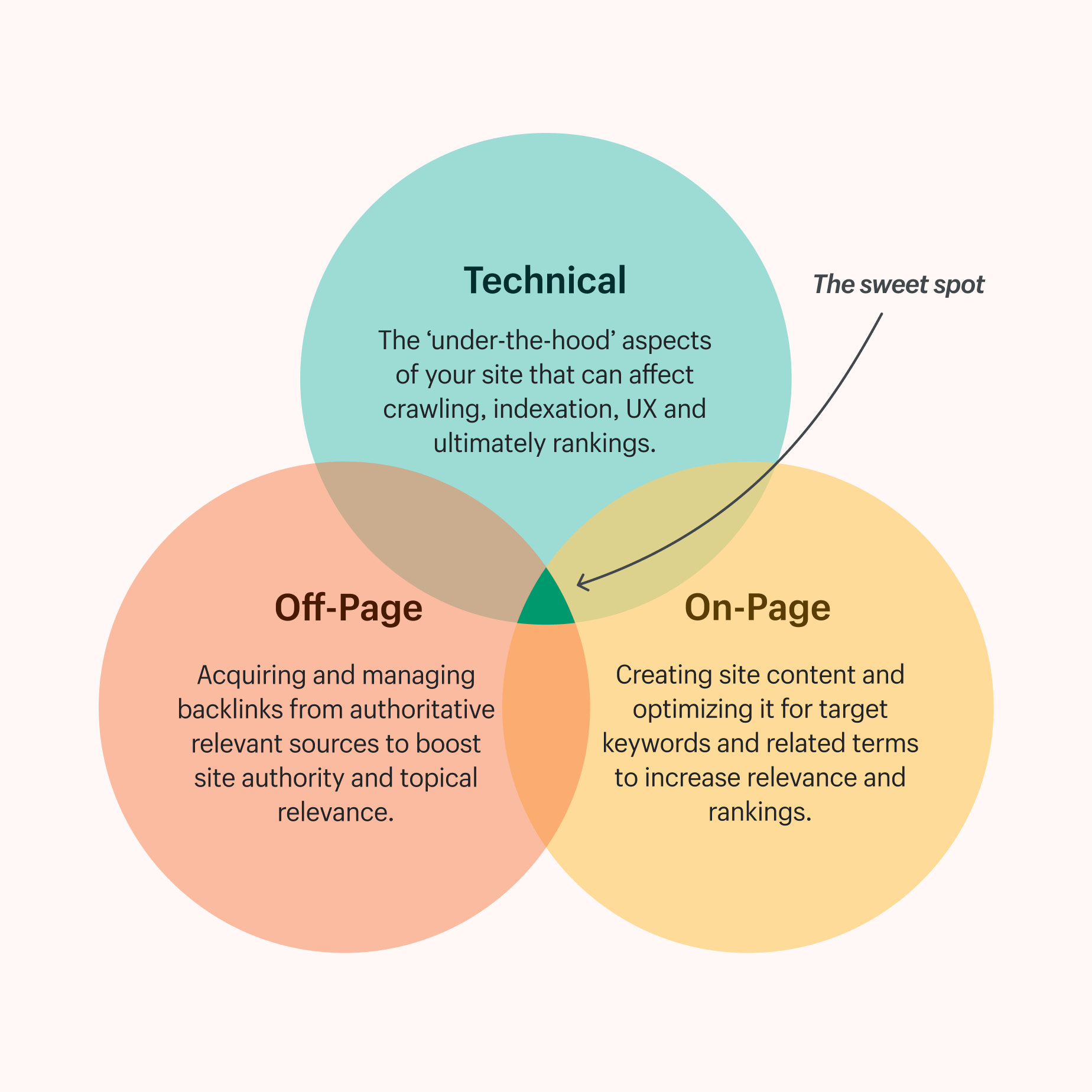
Digital marketers need to know how to get their brands, websites, or companies found by searchers, and understanding the evolution of SEO will keep them on top of their game. It may change in small ways frequently, but its core principles remain the same. We can break SEO down into three basic components or pillars that you should be familiar with – and practice regularly:
Technical Optimization: Technical optimization is the process of improving your SEO without altering your site’s content. It usually happens in the background.
On-Page Optimization: It involves targeting the right keywords within your content and can be done through a content management system. It is the process of ensuring the content on your site is relevant and provides a great user experience. The most common content management systems include WordPress, Wix, Drupal, Joomla, Magento, Shopify, and Expression Engine.
Off-Page Optimization: In the world of Search Engine Optimization, off-page optimization refers to activities outside your site that improve its search engine rankings. Backlinks, for example, help to boost a site’s reputation.
How do search engines actually work?
An algorithm is a computer program that searches for clues in order to give searchers the exact results they are looking for when they have a query and are searching for the answer on the internet. A search engine finds a web page based on a number of factors and decides which web pages to rank for a given keyword based on that search engine algorithm. A search engine works in three stages: crawling, which is the discovery phase; indexing, which is the filing phase; and ranking, which is the retrieval phase.
Ordering and ranking results
Hummingbird is Google’s main search algorithm, and it determines how search engine results are ordered and ranked.
Setting SEO objectives
Choosing SEO objectives is an essential part of any SEO strategy. Setting SEO objectives and aligning them with your business objectives is important for several reasons:
- They encourage buy-in from key stakeholders.
- They help you to formulate your SEO strategy.
- They ensure goals are met.
Examples of SEO objectives
You can use the following examples of SEO objectives to set relevant goals for your own website or business:
This objective focuses on ranking keywords on the first page of Google within nine months.
The purpose of this objective is to increase organic website traffic by 20% in the third quarter and 25% in the fourth quarter.
Increasing SEO market share by 3% to 5% within the next financial year is the goal of this objective.
Setting objectives for different types of businesses

The focus of your objectives will vary depending on whether your business is transactional or informational.
If you are a non-ecommerce commercial site and your business is transactional, your objectives should be tracking sales and lead conversions. If your business is non-ecommerce, your objectives should be lead generation.
You may set objectives centered on brand awareness or website traffic if your business is informational.
Also, SEO is never complete once it is fully implemented. You may need to make changes midway through, play a long game, and wait to see the end results even if you have fully implemented your SEO strategy. When you build a solid SEO foundation – and have a little patience – the benefits of your SEO strategy should become evident, leading to better customer experiences and more conversions for your business.

